11 May Strings in Java
A String is a chain of characters. String Class is provided by Java, and it implements strings as objects of the class String. In this lesson, we will learn about Strings in Java.
There are multiple ways to create a string in Java. Use any of the following constructors:
Create a String
Way 1: The following creates an empty strin using the new:
String student = new String();
Way2: Or, use the following to create an empty string:
String student;
Create a String and initialize
We can also create a string and also initialize it in a single line:
Way 1: The following creates a string and also initialize it:
String message = "Amit";
Way 2: Or, use the following to create and initialize a string using the new:
String message = new String("Amit");
Other Examples
Let us see some other examples:
The following creates a string object. Initialized in the form of an array of characters,
String message = new String(“Studyopedia provides free tutorials!”);
The following is another usage of Strings,
String result = “New York tops the list of most expensive cities for Business”;
Let us see an example of strings,
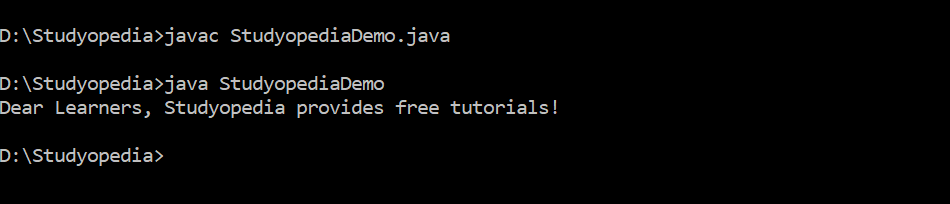
public class StudyopediaDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String message = new String("Studyopedia provides free tutorials!");
System.out.println("Dear Learners, "+message);
}
}
The following is the output,
Let us see how to concatenate two strings,
String Concatenation in Java
To concat a string in Java, use the String concat() method,
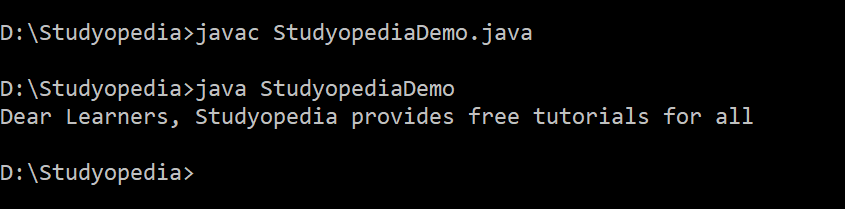
public class StudyopediaDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = new String("Studyopedia provides free tutorials ");
String str2 = str1;
str1 = str1.concat("for all");
System.out.println("Dear Learners, "+str1);
}
}
The following is the output,
Find a specific character in Java
Let us see an example to find a specific character using the contains() function in Java:
// Find a specific character in Java
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String message = "Welcome, Amit";
String subString = "Amit";
boolean res = message.contains(subString);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Output
true
Why are Strings Immutable?
Strings in Java cannot be changed once created. Therefore, String objects are immutable. Remember that this does not apply to reference variables.
An example would make it easier to understand.
String str1 = “Example”;
Now, referred to str2,
String str2 = str1;
The following displays the text Example,
System.out.println(str1); System.out.println(str2);
Now let us use the concat() method,
str1 = str1.concat(“Question”);
Printing str1 displays, Example Question, i.e., concatenation,
System.out.println(str1);
Printing str2, displays, Example,
System.out.println(str2);
Since concatenation did not refer to string str2, the concatenation result is not visible.
Let us now see the methods in the String class that allow you to manipulate strings.
Methods
String class methods allow easier manipulation of strings in Java. Below, the methods are explained with suitable examples.
- char charAt(int index)
Returns the character at the specified index.
- String concat(String str)
Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.
- boolean endsWith(String suffix)
Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.
- boolean equals(Object anObject)
Compares this string to the specified object.
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character.
- int indexOf(String str)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring.
- int lastIndexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the specified character.
- int length()
Returns the length of this string.
Returns a new string resulting from replacing all occurrences of oldChar in this string with newChar.
- boolean startsWith(String prefix)
Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.
- String toLowerCase()
Converts all of the characters in this String to lowercase using the rules of the default locale.
- String toUpperCase()
Converts all of the characters in this String to upper case using the rules of the default locale.
- String trim()
Returns a copy of the string, with leading and trailing whitespace omitted.
Reference: Oracle Java String Class
In this lesson, we learned how to work with Strings in Java.


No Comments