08 Feb Scope of Variables in Java
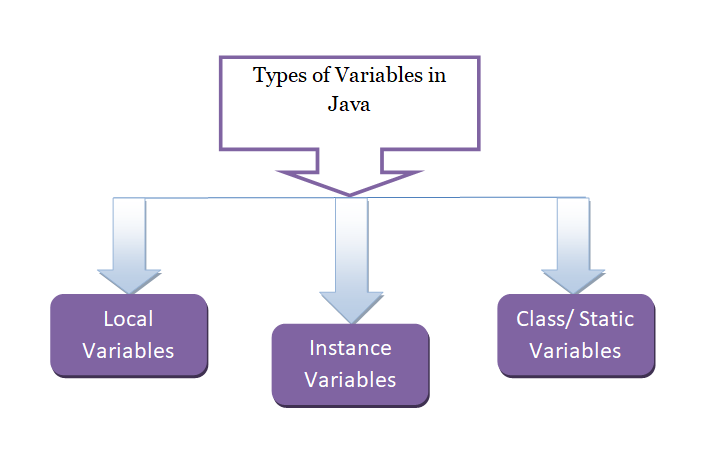
In Java, the scope of a variable refers to the portion of the code where the variable is accessible and can be used. There are several types of variable scopes in Java:
- Local Variables
- Instance Variables
- Class/ Static Variables
Local Variables
A local variable is assigned a value locally. It is a variable that gets declared inside a method and can be accessed inside the same method only. For example,
|
1 2 3 |
int rank = 10; |
Let’s see the complete example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public class StudyopediaDemo { int id = 5; // instance variable static int fees; // static variable void collegeDetails() { int rank = 10; // local variable System.out.println("College Id: " + id); System.out.println("College Rank: " + rank); } public static void main(String args[]) { StudyopediaDemo st = new StudyopediaDemo(); fees = 3000; System.out.println("College Monthly Fees: " + fees); st.collegeDetails(); } } |
Instance Variables
A variable which is declared in a class, but outside the method, is known as instance variable. It is not declared as static.
For example, int id =5;
Let’s see the complete example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public class StudyopediaDemo { int id = 5; // instance variable static int fees; // static variable void collegeDetails() { int rank = 10; // local variable System.out.println("College Id: " + id); System.out.println("College Rank: " + rank); } public static void main(String args[]) { StudyopediaDemo st = new StudyopediaDemo(); fees = 3000; System.out.println("College Monthly Fees: " + fees); st.collegeDetails(); } } |
Class/ Static Variables
A class variable is declared static. Class variable is also known as static variable. For example,
|
1 2 3 |
static int fees; |
Let’s see the complete example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public class StudyopediaDemo { int id = 5; // instance variable static int fees; // static variable void collegeDetails() { int rank = 10; // local variable System.out.println("College Id: " + id); System.out.println("College Rank: " + rank); } public static void main(String args[]) { StudyopediaDemo st = new StudyopediaDemo(); fees = 3000; System.out.println("College Monthly Fees: " + fees); st.collegeDetails(); } } |
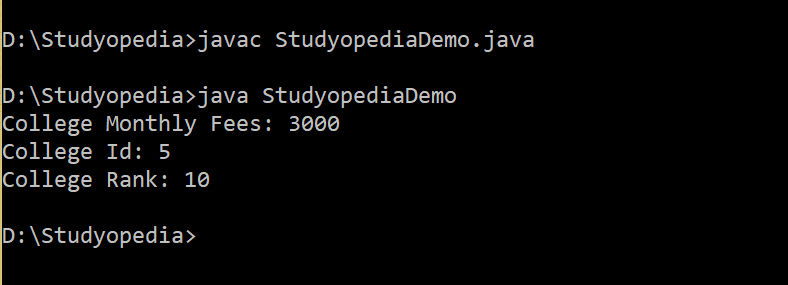
Here’s the output for the above program, which shows the usage of Java variables:
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments