24 Jun Java Variables
In this lesson, we will learn how to work with Java Variables. A variable in Java is a reserved area allocated in memory. It is a container that holds value. Each variable is assigned a type, known as a data type.
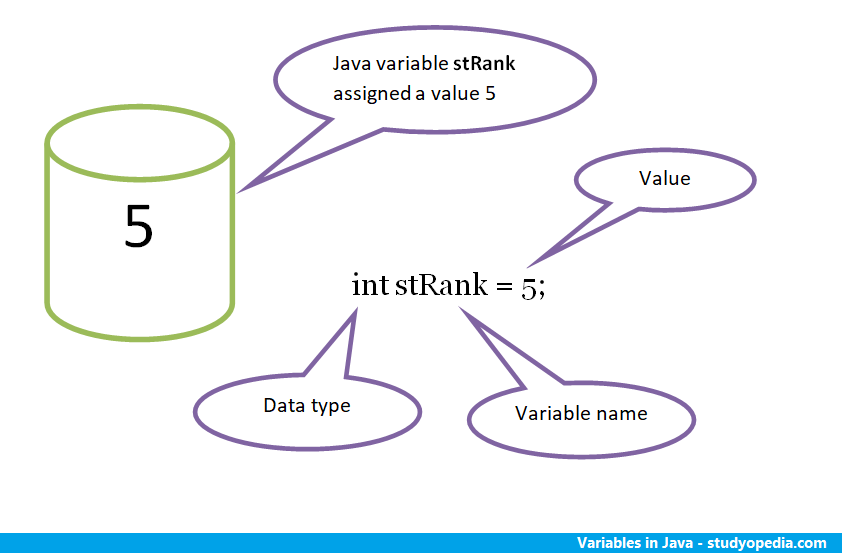
The reserved area set for the variable stRank is shown below. Here, the variable is assigned a value of 5. Also, you can see that we need a data type to declare a variable. The int data type is used below.
Declare Variables in Java
As shown in the figure above, variables are declared by adding a data type to the variable name.
Here are some examples:
int stRank: int score; byte a; boolean result;
Initialize Variables in Java
To initialize a variable, assign a value to it. Here are some examples:
int stRank = 5; int score = 90; byte a = 10; boolean result = true;
Here’s the usage of variables in a Java program:
For example,
public class Studyopedia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 90;
}
}
The value of the integer variable above is assigned 90.


No Comments