21 Jul Java ArrayList
The ArrayList is a Collection class and a part of the java.util package i.e., import the java.util.ArrayList package. It implements the List interface. The size of an ArrayList can be modified i.e., you can easily add or remove elements. This is not the case with Arrays in Java. Once created, you cannot modify the Java Arrays. ArrayList can have duplicate elements.
Let us see some ArrayList methods/ operations with examples:
- Create an ArrayList
- Size of an ArrayList
- Loop through the ArrayList
- Sort an ArrayList
- Access an ArrayList element
- Remove an ArrayList element
Let us first see how to create an ArrayList in Java:
Create and Declare an ArrayList
We can declare an ArrayList using any of the following two ways:
- ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>();
This is called a generic ArrayList. Here, we are giving an example of a String ArrayList. We can create for other types as well. Recommended ✅ - ArrayList myList = new ArrayList();
This is called a raw ArrayList. Discouraged ❎
Let us understand the difference:
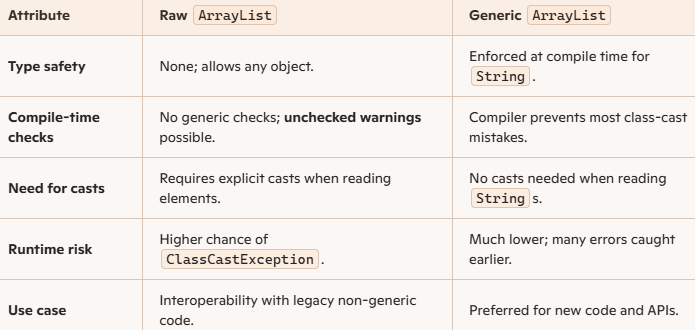
Java – The Recommended way to Create and declare an ArrayList
The recommended way is to declare an ArrayList like this. Here, we are only giving an example of a String ArrayList. You can create it for any type as shown below:
ArrayList<String> myList = new ArrayList<>(); Recommended ✅
Above, we also removed the <String> on the right because the usage of only the Diamond operator <> was introduced in Java 7. Here is why it is preferred now:
- In this case, the compiler infers the type (String) from the variable declaration on the left-hand side.
- Cleaner and less redundant, since you don’t repeat the type.
- Preferred in modern Java code because it improves readability and reduces boilerplate.
Note: In the examples below, we will create and declare an ArrayList like the recommended way.
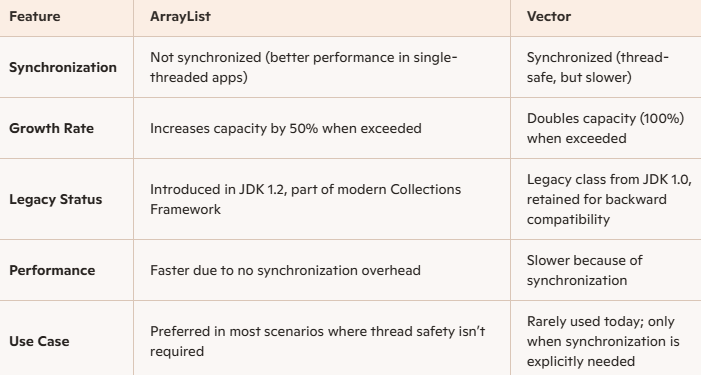
ArrayList vs Vector
Let us see the differences between ArrayList and Vector. Remember, the best choice for general-purpose lists in modern Java applications is an ArrayList.
Example
Let us now see an example and create an ArrayList in Java with string elements:
// Create an ArrayList in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Demo {
static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList myList = new ArrayList<>();
myList.add("Laptop");
myList.add("Tablet");
myList.add("Mobile");
myList.add("TV");
myList.add("Desktop");
System.out.println(myList);
}
}
Output
[Laptop, Tablet, Mobile, TV, Desktop]
Size of an ArrayList
To get the size of an ArrayList i.e., how many elements it has, use the size() method. Let us see an example:
// Get the size of an ArrayList in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Demo {
static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList myList = new ArrayList<>();
myList.add("Laptop");
myList.add("Tablet");
myList.add("Mobile");
myList.add("TV");
myList.add("Desktop");
System.out.println(myList);
System.out.println(myList.size());
}
}
Output
[Laptop, Tablet, Mobile, TV, Desktop] 5
Loop through the ArrayList
Use the for loop to loop through the ArrayList in Java. Let us see an example:
// Loop through the ArrayList in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Demo74 {
static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList myList = new ArrayList<>();
// adding values
myList.add("Laptop");
myList.add("Tablet");
myList.add("Mobile");
myList.add("TV");
myList.add("Desktop");
System.out.println(myList);
// Loop through the ArrayList
for(int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++){
System.out.println(myList.get(i));
}
}
}
Output
[Laptop, Tablet, Mobile, TV, Desktop] Laptop Tablet Mobile TV Desktop
Loop through the ArrayList (Get the elements from the user)
Let us see an example to loop through the ArrayList, but we will get the elements from the user using the Scanner class:
// Loop through the ArrayList in Java (Get the elements from the user)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Demo73 {
static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList myList = new ArrayList<>();
// Ask user
System.out.println("Enter 5 devices: ");
int n = 5;
first: for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
String device;
while(true) {
System.out.println("Enter the device " + (i + 1) + ": ");
device = sc.nextLine();
if (!device.isEmpty()) {
myList.add(device);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid input");
break first;
}
}
// myList.add(device);
}
// Loop through the ArrayList
for(int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++){
System.out.println(myList.get(i));
}
/*
myList.add("Laptop");
myList.add("Tablet");
myList.add("Mobile");
myList.add("TV");
myList.add("Desktop");
*/
}
}
Output
Enter 5 devices: Enter the device 1: Laptop Enter the device 2: Desktop Enter the device 3: Tablet Enter the device 4: TV Enter the device 5: Notebook Laptop Desktop Tablet TV Notebook
Sort an ArrayList
To sort an ArrayList in Java, use the Collections.sort() method. Let us see an example:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class Studyopedia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an ArrayList with string elements
ArrayList<String> sports = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding string elements
sports.add("Cricket");
sports.add("Football");
sports.add("Tennis");
sports.add("Badminton");
sports.add("Basketball");
sports.add("Volleyball");
// Display the ArrayList
System.out.println(sports);
// Sort the ArrayList
Collections.sort(sports);
System.out.println("\nSorted ArrayList...");
// Loop through the sorted ArrayList
for (int i = 0; i < sports.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Element "+(i+1)+" = "+sports.get(i));
}
}
}
Output
[Cricket, Football, Tennis, Badminton, Basketball, Volleyball] Sorted ArrayList... Element 1 = Badminton Element 2 = Basketball Element 3 = Cricket Element 4 = Football Element 5 = Tennis Element 6 = Volleyball
Access an ArrayList element
To access an element of an ArrayList, use the get() method. Set the index number of the element you want to access as a parameter of the get() method. For example, to access the 3rd element, set index 2 i.e.:
sports.get(2)
To access the 5th element, set index 4 i.e.:
sports.get(4)
Let us now see an example to access an element of an ArrayList in Java:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class Studyopedia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an ArrayList with string elements
ArrayList<String> sports = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding string elements
sports.add("Cricket");
sports.add("Football");
sports.add("Tennis");
sports.add("Badminton");
sports.add("Basketball");
sports.add("Volleyball");
// Display the ArrayList
System.out.println(sports);
// Access elements
System.out.println("Element 1 = "+sports.get(0));
System.out.println("Element 2 = "+sports.get(1));
System.out.println("Element 3 = "+sports.get(2));
}
}
Output
[Cricket, Football, Tennis, Badminton, Basketball, Volleyball] Element 1 = Cricket Element 2 = Football Element 3 = Tennis
Remove an ArrayList element
To remove an element from an ArrayList, use the remove() method. Set the index number of the element you want to remove as a parameter of the remove () method. For example, to remove the 3rd element, set index 2 i.e.:
sports.remove(2)
To access the 5th element, set index 4, i.e.:
sports.remove(4)
Let us now see an example of removing elements from an ArrayList in Java:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class Studyopedia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an ArrayList with string elements
ArrayList<String> sports = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding string elements
sports.add("Cricket");
sports.add("Football");
sports.add("Tennis");
sports.add("Badminton");
sports.add("Basketball");
sports.add("Volleyball");
// Display the ArrayList
System.out.println("ArrayList = "+sports);
// Remove two elements
sports.remove(0);
sports.remove(1);
System.out.println("Updated ArrayList = "+sports);
}
}
Output
ArrayList = [Cricket, Football, Tennis, Badminton, Basketball, Volleyball] Updated ArrayList = [Football, Badminton, Basketball, Volleyball]
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now


No Comments