08 May Arrays in Java
Array is a collection of elements, of fixed size and type, for example, collection of 10 elements of type int. It is a data structure to group elements. In this lesson, we will learn how to work with arrays in Java Programming Language. Arrays in Java use index to access an element.
Here, we will discuss about one-dimensional and multidimensional arrays,
One-Dimensional Arrays
Arrays with a single dimension are one-dimensional arrays in Java. Let us see how to declare 1D arrays in Java:
Declaration and Initialization
For declaring one-dimensional array in Java Programming, you need to specify the datatype and the variable name like the following,
|
1 2 3 |
datatype variable_name[]; |
Above, datatype is the type of data you want the elements to be
variable_name is the name of the variable
The following example shows the correct way of declaring arrays in Java,
|
1 2 3 |
int marks; |
Above is an array of int. Here, we saw how to declare an array variable, with our variable name, marks. To create an array in Java and initialize it, use the new operator,
|
1 2 3 |
variable_name = new datatype[size]; |
Above,
Using new to allocate an array, specify the type and how many elements you want.
variable_name: name of the variable
datatype[size]: creates a new array
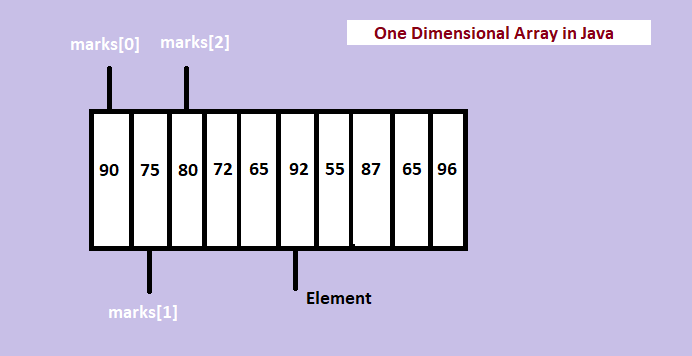
Let us see an example that allocates 10 element array of integers and assigns reference of the array to the variable marks. These 10 elements are the marks of 10 students in a subject,
|
1 2 3 |
marks = new int[10]; |
Now our array looks like,
|
1 2 3 4 |
int marks; marks = new int[10]; |
Let us learn how to assign value to the elements. The indexes in array start with 0.
Right now, we have space for 10 elements. Add the index in the square brackets and insert value to the specified element, like
The following assigns the value 90 to the first element,
|
1 2 3 |
marks[0] = 90; |
The following assigns the value 75 to the second element,
|
1 2 3 |
marks[1] = 75; |
The following assigns the value 80 to the third element,
|
1 2 3 |
marks[2] = 80; |
We can also assign values to elements like,
|
1 2 3 |
int marks[] = {90, 75, 80, 72, 65, 92, 55, 87, 65, 96}; |
Let us see what we have done till now,
As we saw above, add all the elements and run the entire example below,
First Array Program in Java
Showing the usage of one-dimensional array to add marks of 10 students,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
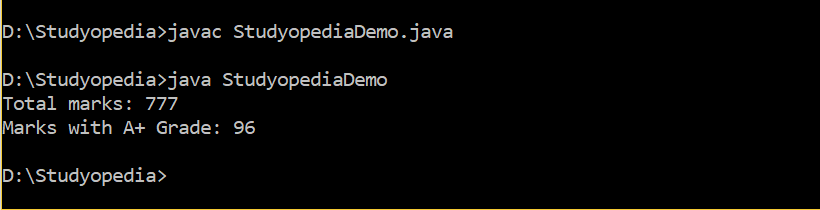
public class StudyopediaDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { int marks[], result = 0; // array created marks = new int[10]; // assigning values to elements marks[0] = 90; marks[1] = 75; marks[2] = 80; marks[3] = 72; marks[4] = 65; marks[5] = 92; marks[6] = 55; marks[7] = 87; marks[8] = 65; marks[9] = 96; // Adding marks of all students for (int i = 0; i < marks.length; i++) { result+= marks[i]; } System.out.println("Total marks: " +result ); System.out.println("Marks with A+ Grade: " +marks[9]); } } |
The following is the output of the above example,
In this lesson, we learned arrays in Java and how to work with one-dimensional arrays. Multi-Dimensional Arrays are discussed in the next lesson.


No Comments