06 Jul Python Operators with Examples
Python Operators perform operations by taking one or more values to give another value. These operations are performed on variables and values. The following are the operators:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Comparison/ Relational operators
- Identity Operators
- Membership Operators
- Bitwise Operators
The types of operators are explained here with examples, where x = 5, y =10. The following are the Python operators:
Arithmetic Operators
Let us see the table below describing the Arithmetic operators with examples:
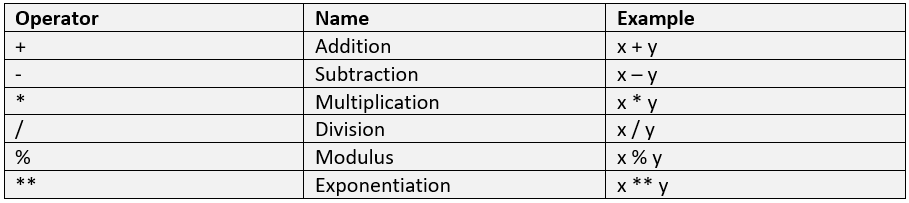
Let us see an example:
Demo8.py
# Arithmetic Operators in Python # Code by studyopedia a = 10 b = 6 print(a + b) print(a - b) print(a * b) print(a / b) print(a % b)
Output
16 4 60 1.6666666666666667 4
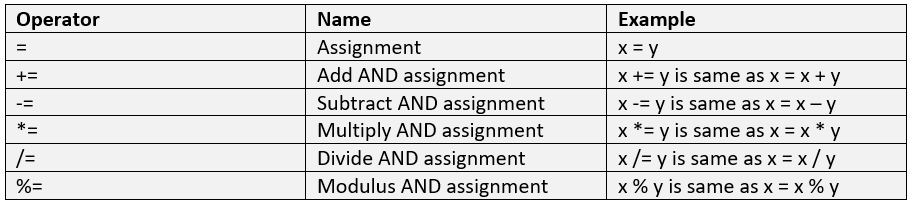
Assignment Operators
To assign values to variables, use the Assignment operators. Let us see the table below describing Assignment operators with examples:
Let us see an example:
Demo9.py
# Assignment Operators in Python # Code by studyopedia a = 10 print(a) a +=5 # a = a + 5 print(a) a -=3 # a = a - 3 print(a) a *=2 # a = a * 2 print(a)
Output
10 15 12 24
Comparison/ Relational operators
To compare the value of two operands, Python has comparison operators, i.e., relational operators. Let us see the table below describing comparison operators with examples:
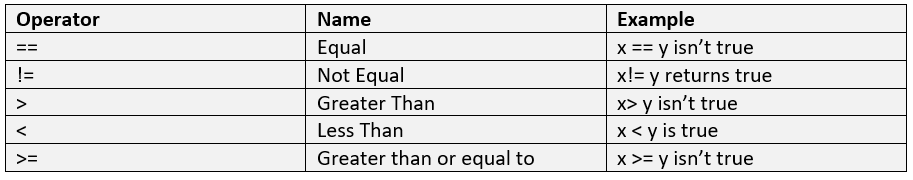
Logical operators
Logical operators combine conditional statements. Let us see the table below describing logical operators with examples:

Let us see an example:
Demo10.py
# Logical Operators in Python # Code by studyopedia a = 10 # AND Operator res = a > 5 and a < 20 print(res) # OR Operator res = a < 5 or a > 8 print(res) # NOT operator res = not(a > 5 and a < 20) print(res)
Output
True True False
Identity Operators
To compare the objects to check they are in the same memory location, work with the Python Identity operators. Let us see the table below describing Identity Operators in Python:

Let us see an example:
Demo11.py
# Identity Operator in Python # Code by studyopedia a = ["John","Amit","Tom"] b = ["John","Amit","Tom"] c = a # IS operator print(a is c) # IS NOT Operator print(a is not c) # IS NOT Operator print(a is not b)
Membership Operators
The Membership operator is used to check for membership in a data structure, like a tuple, string, list, dictionary, etc. Let us see the table below describing Membership operators with examples:
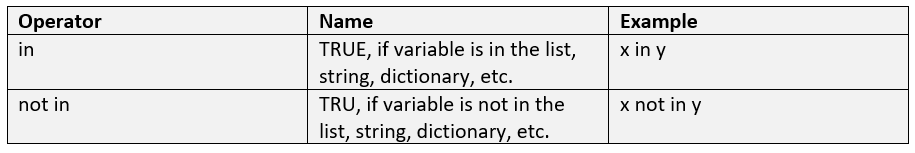
Let us see an example:
Demo12.py
# Membership Operators in Python
# Code by studyopedia
a = ["Amit","John","Tim"]
# IN operator
print("Amit" in a)
# NOT IN operator
print("Smith" not in a)
# NOT IN operator
print("John" not in a)
Bitwise Operators
To compare Binary numbers, bit by bit, on operands, use the Bitwise Operators. The following are the Bitwise Operators:
- Binary AND
- Binary OR
- Binary XOR
- Binary NOT
- Binary Left Shift
- Binary Right Shift
Binary AND Bitwise operator
The Binary AND operator sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1, i.e., if both the operands are 1, then the result is 1.
Let us see an example:
## Bitwise AND operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
y = 11 # 11 = 0000 1011
res = 0
res = x & y;
print ("x AND y = ", res)
The output is as follows:
x AND y = 2
Binary OR Bitwise operator
The Binary OR operator sets each bit to 1 if any of the two bits are 1,i.e., if any of the two operands are 1, then the result is 1.
Let us see an example:
## Bitwise OR operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
y = 11 # 11 = 0000 1011
res = 0
res = x | y;
print ("x OR y = ", res)
The output is as follows:
x OR y = 27
Binary XOR Bitwise operator
The Binary XOR operator sets each bit to 1 if only one of them is 1, i.e., if only one of the two operands is 1.
Let us see an example:
## Bitwise XOR operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
y = 11 # 11 = 0000 1011
res = 0
res = x ^ y;
print ("x XOR y = ", res)
The output is as follows:
x XOR y = 25
Binary NOT Bitwise operator
The Binary NOT Bitwise operator negates the bits, i.e., 1 for 0 and 0 for 1.
Let us see an example:
## Bitwise NOT operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
res = 0
res = ~x
print (" ~x = ", res)
The output is as follows:
~x = -19
Binary LEFT SHIFT Bitwise operator
The Binary LEFT SHIFT operator shifts the left operand value to the left, by the number of bits in the right operand. The leftmost bits while shifting fall off.
Let us see an example to implement the LEFT SHIFT Bitwise Operator and shift 3 times:
## Bitwise Left Shift operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
res = 0
res = x << 3
print (" Left Shift = ", res)
The output is as follows:
Left Shift = 144
Now, let us see how the above result was calculated. We have to shift 3 times left and fill zero on the right:
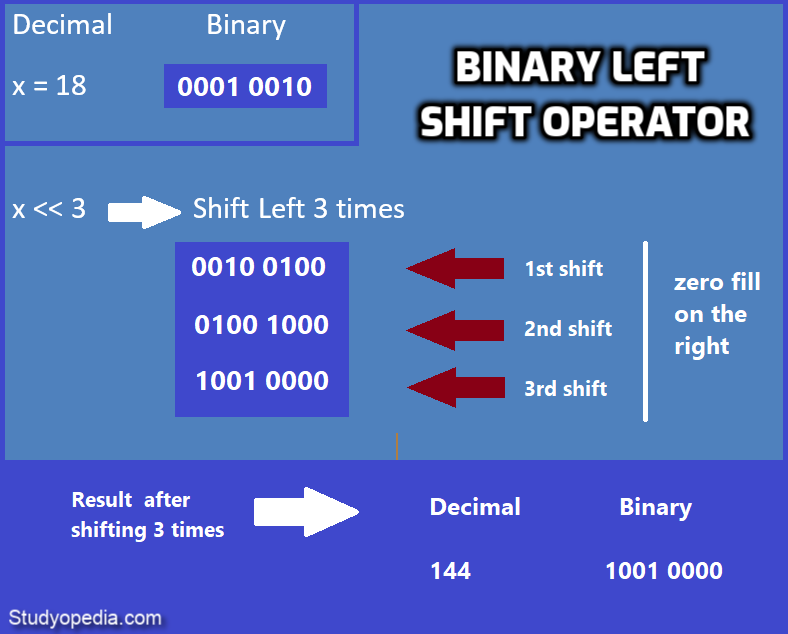
Binary RIGHT SHIFT Bitwise operator
The Binary RIGHT SHIFT operator shifts the left operand value to the right, by the number of bits in the right operand. The rightmost bits while shifting fall off.
Let us see an example to implement the RIGHT SHIFT Bitwise operator and shift 2 times:
## Bitwise Right Shift operator
x = 18 # 18 = 0001 0010
res = 0
#shift 2 times
res = x >> 2
print (" Right Shift = ", res)
The output is as follows:
Right Shift = 4
Bitwise Operators ( Final Coding Example)
Let us see a single example to understand all the bitwise operators discussed above:
Demo13.py
# Bitwise Operators in Python # Code by studyopedia a = 18 #18 = 0001 0010 b = 11 #11 = 0000 1011 res = 0 ## Bitwise AND res = a & b print(res) ## Bitwise OR res = a | b print(res) ## Bitwise XOR res = a ^ b print(res) ## Bitwise NOT res = ~a print(res) ## Left shift bitwise operator res = a << 3 print(res) ## Right shift bitwise operator res = a >> 2 print(res)
Output
2 27 25 -19 144 4
Python Tutorial (English)
Python Tutorial (Hindi)
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website, Studyopedia, with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments