24 Sep C++ Data Types
Like many other programming languages, such as Java, Python, etc; Variables in C++ also store data of different types. These are classified under C++ data types. Let us understand the built-in and user-defined types in C++ language:
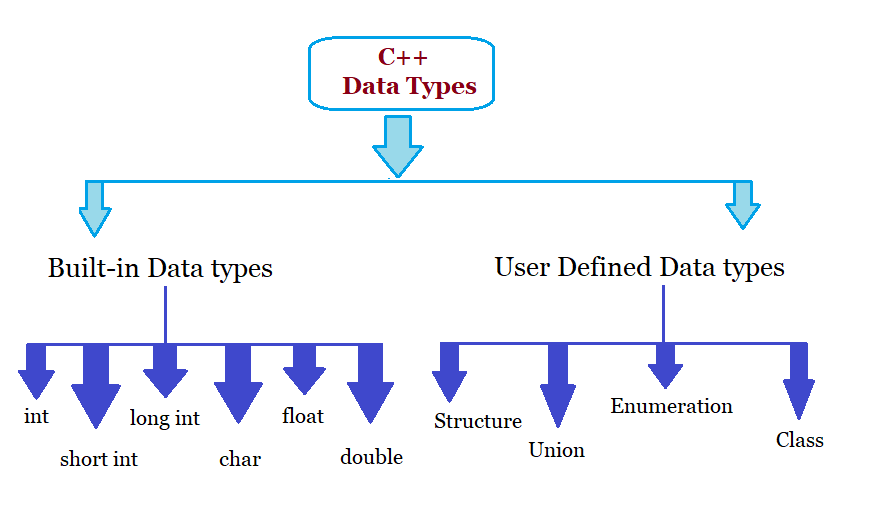
C++ Data types include string, int, short int, float, and other types. Let’s see some data types in C++, one by one.
Built-in Data types
The following are the built-in datatypes and the datatypes, which will be used while declaring variables.
int
Data Type: int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: -32768 to 32767
Data Type: unsigned int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: 0 to 65535
Data Type: signed int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: -31768 to 32767
short int
Data Type: short int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: -31768 to 32767
Data Type: unsigned short int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: 0 to 65535
Data Type: signed short int
Size: 2 bytes
Range: -32768 to 32767
long int
Data Type: long int
Size: 4 bytes
Range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
Data Type: unsigned long int
Size: 4 bytes
Range: 0 to 4294967295
Data Type: signed long int
Size: 4 bytes
Range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
char
Data Type: char
Size: 1 byte
Range: -128 to 127
float
Data Type: float
Size: 4 bytes
Range: 3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38
double
Data Type: double
Size: 8 bytes
Range: 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308
Data Type: long double
Size: 10 bytes
Range: 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932
User-Defined Data types
The following are the user-defined data types,
Structure
The struct keyword is used to declare a structure. The structure is a collection of different data types. Different memory locations are allocated for all the members.
Here’s an example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
struct Players { char name; int rank; int age; } |
Union
Union is also a collection of different data types. The union keyword is used to declare a union. Common memory locations are allocated for all the members, unlike structures, which allocate different memory locations.
Let’s see the difference between Structures and Unions,
Structures Example
Here the size of p1 is 7 i.e. different memory locations allocated,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
struct Players { char name; // 1 int rank; // 2 float average; // 4 } p1; |
Unions Example
Here the size of p1 is 4 i.e. the maximum size, common memory locations are allocated.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
union Players { char name; // 1 int rank; // 2 float average; // 4 } p1; |
Class
The user-defined datatype class is used to declare variables. Objects are class variables.
Classes are discussed in the C++ classes & objects lesson.
Enumeration
If you want to attach names to numbers, then use the enumerated data type. To add an enumerated data type, use the enum keyword. You can assign values in the form of 0,1,2,3, etc.
|
1 2 3 |
enum device {laptop, mobile, desktop, tablet}; |
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others:
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments