14 Mar Precision in Machine Learning
Let’s dive into Precision, one of the key evaluation metrics for classification models. Precision is particularly important when the cost of false positives is high. It helps answer the question: “Of all the positive predictions made by the model, how many were actually correct?”
What is Precision in Machine Learning
Precision measures the proportion of true positive predictions (correctly predicted positive cases) out of all positive predictions made by the model (both true positives and false positives). It focuses on the accuracy of the positive predictions.
Formula of Precision
Precision is calculated using the following formula:

When to Use Precision
Precision is a critical metric when:
- False Positives are Costly:
- Example: In spam detection, incorrectly flagging a legitimate email as spam (false positive) is costly because it might cause the user to miss important emails.
- Focus on Positive Class:
- When the positive class is the primary focus (e.g., detecting diseases, fraud, or rare events).
- Imbalanced Datasets:
- When the dataset is imbalanced, and the positive class is rare, precision helps ensure that the model’s positive predictions are reliable.
Example of Precision
Let’s say you have a binary classification problem where you’re predicting whether an email is spam (Positive) or not spam (Negative). After evaluating your model, you get the following results:
- True Positives (TP): 90 (spam emails correctly identified as spam).
- False Positives (FP): 10 (legitimate emails incorrectly flagged as spam).
Using the formula:
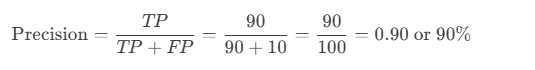
This means that 90% of the emails predicted as spam were actually spam.
Advantages of Precision
- Focus on Positive Predictions:
- Precision ensures that the model’s positive predictions are accurate, which is critical in applications where false positives are costly.
- Useful for Imbalanced Datasets:
- When the positive class is rare, precision helps evaluate how well the model identifies the positive class without being overwhelmed by the majority class.
Limitations of Precision
While precision is useful, it has some limitations:
- Ignores False Negatives:
- Precision doesn’t account for false negatives (missed positive cases). A model with high precision might still miss many actual positive cases.
- Trade-off with Recall:
- Increasing precision often reduces recall (the ability to identify all positive cases), and vice versa. This is known as the precision-recall trade-off.
When Not to Use Precision
Avoid using precision when:
- False Negatives are Costly:
- If missing positive cases (false negatives) is more costly than false positives, precision alone is not sufficient. Use recall or F1-score instead.
- Balanced Classes:
- If the dataset is balanced and both false positives and false negatives are equally important, accuracy might be a better metric.
Precision in Context: Precision-Recall Trade-off
Precision is often evaluated alongside recall (the ability to identify all positive cases). There’s a trade-off between the two:
- High Precision: Fewer false positives, but more false negatives (missed positives).
- High Recall: Fewer false negatives, but more false positives.
The choice between precision and recall depends on the problem:
- High Precision: Important in spam detection, where false positives are costly.
- High Recall: Important in medical diagnosis, where false negatives (missing a disease) are costly.
Hands-On Example of Precision
Let’s calculate precision using Python and Scikit-learn:
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
# True labels
y_true = [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0] # 0 = Not Spam, 1 = Spam
# Predicted labels
y_pred = [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0] # Model's predictions
# Calculate precision
precision = precision_score(y_true, y_pred)
print(f"Precision: {precision * 100:.2f}%")
Output
Precision: 75.00%
Key Takeaways
- Precision measures the proportion of true positive predictions out of all positive predictions.
- It’s a critical metric when false positives are costly (e.g., spam detection, fraud detection).
- Precision is often evaluated alongside recall, and there’s a trade-off between the two.
- Use precision when the focus is on ensuring that positive predictions are accurate.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:
- NLP Tutorial
- Generative AI Tutorial
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Ollama Tutorial
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Tutorial
- Copilot Tutorial
- Gemini Tutorial
- ChatGPT Tutorial


No Comments