01 Oct Unsupervised Machine Learning
In unsupervised learning, the model identifies patterns and relationships in the input without any prior knowledge about the data, unlike supervised learning. That means, their no training data.
The machine learning model is given unlabeled data in unsupervised learning and allows identifying and discovering patterns and insights on their own. This process is without explicit instruction.
Example: The unsupervised ML Model is used to identify spam emails from your email account.
Example: Customer Segmentation
You’re running an ecommerce retail store. You have lots of customers. This data such as age, location, purchase history, browsing behavior, etc. is to be understood, but you do not have any predefined labels or categories for them.
In this case, unsupervised learning can be used to fit marketing strategies and product recommendations to different segments. It’s like discovering hidden patterns in your customer base without any prior labeling.
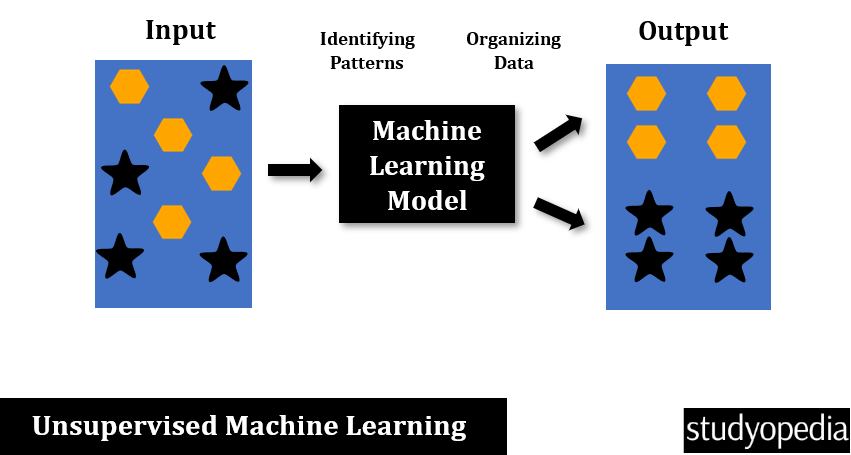
Let us see an example. Our data includes Hexagon and Star shapes. The below image demonstrates a machine learning unsupervised learning process to identify patterns and organize the data:
- Input: On the left side, we have our “Input,” there are various shapes scattered: four hexagons, and four star shapes.
- Machine Learning Model: In the center, we have our model that identifies patterns and relationships in the input.
- On the right side, labeled “Output,” the shapes are organized into groups: four hexagons, and four star shapes.
The below image visually represents how a machine learning algorithm can take unorganized input data, identify patterns within it, and produce organized output data.
The following are the types of Unsupervised Learning:
- Clustering
- Association
Clustering
The clustering algorithm will analyze the data and group similar data points together, such as analyzing the customer data group similar customers into clusters based on their purchasing behavior.
Here are some examples of Clustering:
- Customer Segmentation: Grouping customers based on purchase behavior for targeted marketing.
- Image Segmentation: Dividing an image into segments based on pixel similarity for object recognition.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual data points that do not fit into any cluster, is useful for fraud detection.
Association
In this, the patterns of associations are identified between different variables or items.
Here are some examples of Association:
- Market Basket Analysis: Finding associations between products purchased together, such as how bread and butter are often bought together.
- Web Usage Mining: Analyzing user behavior patterns on websites to enhance user experience and design.
Clustering vs Association
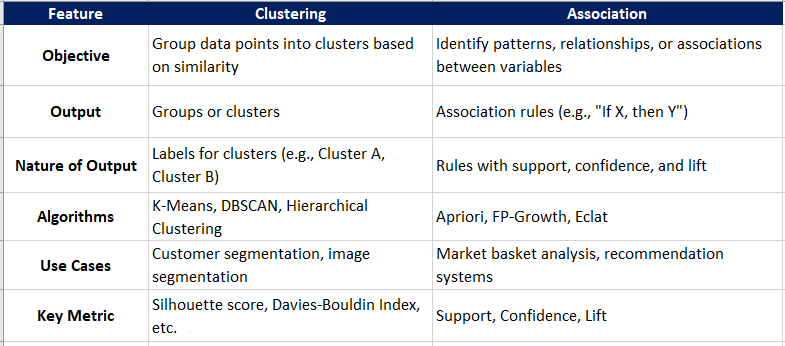
Both the classification and regression concepts will be discussed later in the Machine Learning – Clustering and Machine Learning – Association sections.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments