25 Feb JavaScript Math
The Math object in JavaScript has properties and methods for mathematical calculations. We will understand them one by one with examples.
JavaScript Math Properties
The following are some of the Math properties:
- PI
- SQRT2
- LN2
- LN10
Let us understand the properties one by one with examples.
Math.PI Property
The Math.PI property returns the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Let us see an example to implement Math.PI Property:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Property</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Math.PI = "+Math.PI; </script> </body> </html> |
Output

Math.SQRT2 Property
The Math.SQRT2 property returns the square root of 2. Let us see an example to implement Math.SQRT2 Property:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Property</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Math.SQRT2 = "+Math.SQRT2; </script> </body> </html> |
Output

Math.LN2 Property
The Math.LN2 property returns the natural logarithm of 2. Let us see an example to implement Math.LN2 Property:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Property</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Math.LN2 = "+Math.LN2; </script> </body> </html> |
Output

Math.LN10 Property
The Math.LN2 property returns the natural logarithm of 10. Let us see an example to implement Math.LN10 Property:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Property</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Math.LN10 = "+Math.LN10; </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript Math Methods
The following are some of the mathematical methods:
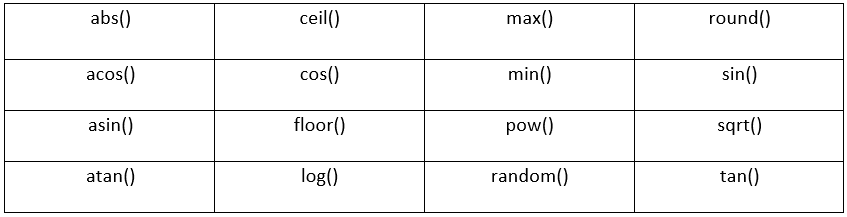
Let us understand the Math methods one by one with examples.
JavaScript abs() method
The abs() method is used to return the absolute value of a number in JavaScript. Let us see an example to implement the abs() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h2>JavaScript Math Function</h2> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "abs(-5) = "+Math.abs(-5); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript ceil() method
The ceil() method is used to return the smallest integer value, greater than or equal to a specific number. Let us see an example to implement the ceil() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "ceil(22.35) = "+Math.ceil(22.35); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript max() method
The max() method is used to return the maximum value from the given numbers in JavaScript. Let us see an example to implement the max() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "max(10, 18, 25, -8, -1, 15) = "+Math.max(10, 18, 25, -8, -1, 15); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript min() method
The min() method is used to return the minimum value from the given numbers in JavaScript. Let us see an example to implement the min() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "min(10, 18, 25, -8, -1, 15) = "+Math.min(10, 18, 25, -8, -1, 15); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript round() method
The round() method is used to round a given number’s value to the nearest integer. Let us see an example to implement the round() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "round(15.6) = "+Math.round(15.6); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript acos() method
The acos() method is used to return the arccosine of a specific number in radians. Let us see an example to implement the acos() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>acos(0) = "+Math.acos(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript cos() method
The cos() method is used to return the cosine of a specific number in JavaScript. Let us see an example to implement the cos() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>cos(0) = "+Math.cos(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript sin() method
The sin() method is used to return the sine of a specific number in radians. Let us see an example to implement the sin() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>sin(0) = "+Math.sin(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript asin() method
The asin() method is used to return the arcsine of a specific number in radians. Let us see an example to implement the asin() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>asin(0) = "+Math.asin(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output
JavaScript floor() method
The floor() method is used to return the largest integer value, smaller than or equal to a specific number. Let us see an example to implement the floor() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "floor(22.35) = "+Math.floor(22.95); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript pow() method
The pow() method is used to return the base to the exponent power. Let us see an example to implement the pow() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Math.pow(5,2) = "+Math.pow(5,2); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript sqrt() method
The sqrt() method is used to return the square root of a specific number. Let us see an example to implement the sqrt() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "sqrt(49) = "+Math.sqrt(49); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript atan() method
The atan() method is used to return the arc tangent of a specific number in radians. Let us see an example to implement the atan() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>atan(0) = "+Math.atan(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript tan() method
The tan() method is used to return the tangent of a specific number in JavaScript.
Let us see an example to implement the tan() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "<p>tan(0) = "+Math.tan(0); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript log() method
The log() method is used to return the natural logarithm of a specific number in JavaScript. Let us see an example to implement the log() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "log(1) = "+Math.log(1); </script> </body> </html> |
Output

JavaScript random() method
The random() method is used to return a random number between 0 and 1. Here, 0 is inclusive, and 1 is exclusive. Let us see an example to implement the random() method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>JavaScript Math Function</h1> <p id="test"></p> <script> document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "random() = "+Math.random(); </script> </body> </html> |
Output



No Comments