22 Jan C++ Classes and Objects
In this lesson, we will understand what is a class and object. With that, we will also see some examples to create classes and objects. In C++, a class is a template for an object, whereas an object is an instance of a class.
What is a Class in C++
C++ is an Object-Oriented Programming Language. It is an extension of the C Programming Language i.e., C with Classes. Consider, a class as a blueprint.
Create a Class
To create a class is to declare in C++. At first, to declare a class, use the class keyword in C++. The class is a reserved word in C++.
Let us now see how to define a class in C++. The public is an access specifier in C++. For the public access specifier, the members can be accessed from outside the class easily. In the below example, the class members are length and width:
class Rectangle {
public:
double length;
double width;
}
What is an Object In C++
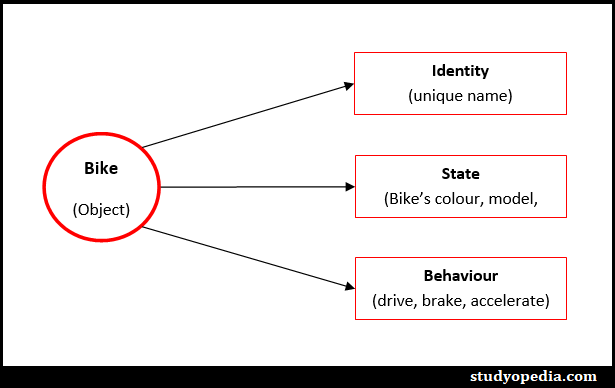
An object is an instance of a class i.e., an object is created from a class. Object represents real-life entities, for example, a Bike is an object. Object has State, Behavior, and Identity:
- Identity: Name of Bike
- State (Attributes): The data of object Bike i.e., Color, Model, Weight, etc.
- Behavior (Methods): Behavior of object Bike like to Drive, Brake
Let us now see the representation, with Bike as an object:
Create an Object
An object is a runtime entity with state and behavior. To create an object in C++, we use a Class. The syntax is as follows:
ClassName obj;
Above, we have set the class name with ClassName followed by the object obj. This is how an object is created in C++.
Let us see the above example and create three objects in C++:
// Create objects of class Rectangle // Declaring rect1, rect2, rect3 of type Rectangle Rectangle rct1; Rectangle rct2; Rectangle rct3;
Example: Classes and Objects
Let us see the complete example to create a class and object. In this example, we will also learn how to access the attributes of the class using the dot:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rectangle {
// Access Specifier
public:
double length; // Attribute1
double width; // Attribute2
};
int main() {
// Creating an object rct
// Declaring rct of type Rectangle
Rectangle rct;
double area;
// Accessing attributes
// Set the values of length and width
rct.length = 25;
rct.width = 20;
cout <<"\nLength of Rectangle = "<<rct.length;
cout <<"\nWidth of Rectangle = "<<rct.width;
// Calculating Area of Rectangle
area = rct.length * rct.width;
cout<<"\n\nArea of Rectangle = "<<area;
}
Output
Length of Rectangle = 25 Width of Rectangle = 20 Area of Rectangle = 500
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now


No Comments