24 Apr Transmission Impairments in Data Communication
Whenever a signal is sent from sender, the receiver in the same form may not receive it. It can be somewhat different, due to flaws in the media, used to send it. To understand it better, transmission impairments in data communication are divided into the following three categories,
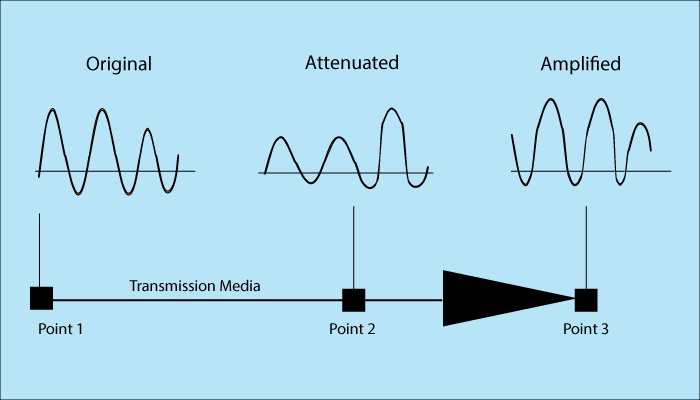
Attenuation
Whenever a signal passes, it faces loss of energy. This happens to overcome the resistance of medium.
To compensate the signal loss, amplifiers are used. Amplifiers amplify the signal.
Noise
As the name tells, Noise is a random fluctuation in a signal. It is an undesirable electrical energy, which is annoying.
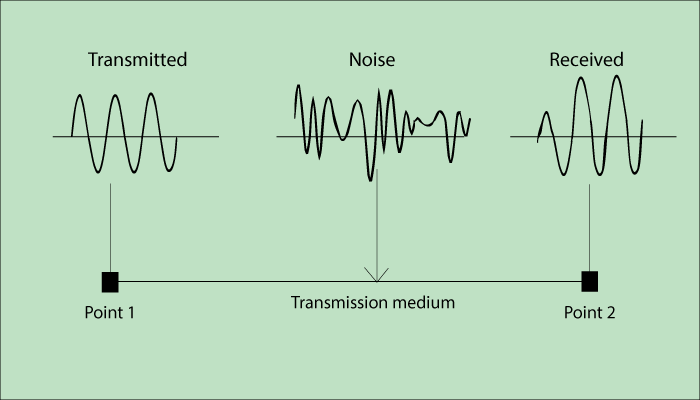
The following are the three types of Noise:
- Thermal Noise
- Induced Noise
- Crosstalk
Thermal Noise:
Random motion of electrons in a wire creates extra signal.
Induced Noise:
The noise comes from motors.
Crosstalk:
The noise comes when another wire affects a wire.
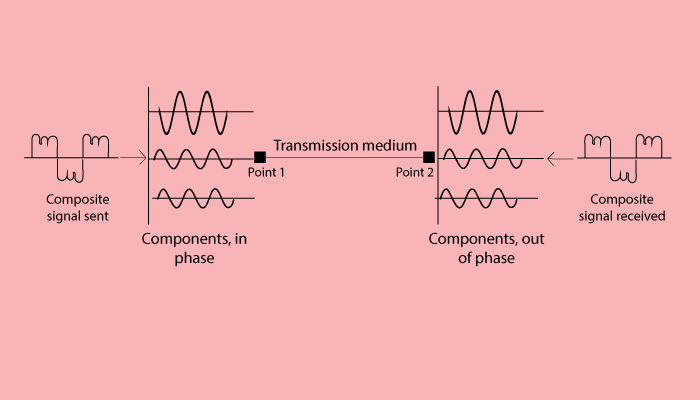
Distortion
When signal changes its form, it is known as distortion. If at the receiving end, the components are out of phase, it means distortion occurred.
In the example below, Point1 is connected to Poin2 with a Transmission Medium.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now


No Comments