10 Aug Computer Networks Transmission Modes
Transmission modes in Computer Networks transfers data between two devices and it also defines the direction of signal flow between them. In the previous lesson, we learned about Line Configuration in Computer Networks.
The following are the types of Transmission Modes.
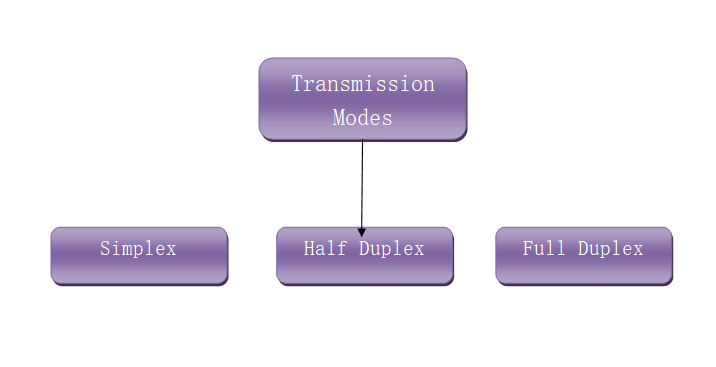
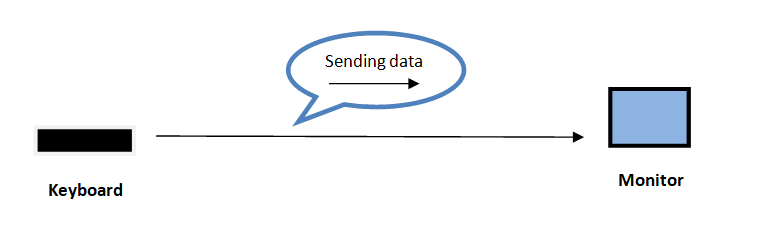
Simplex Transmission Mode
Simplex mode is a mode when one device always acts as a sender and another always act as a receiver. It means the direction of signal flow is the same i.e. unidirectional.
For example, Mouse and monitor, Mouse for input, whereas Monitor for receiving output.
Another example can be, Keyboard and Monitor
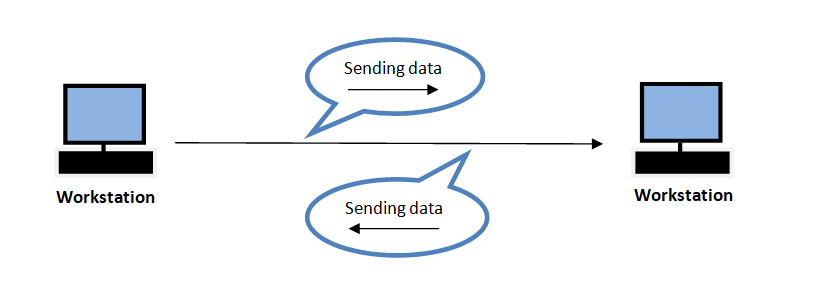
Half Duplex Transmission Mode
Half Duplex mode is a mode when either of the device acts as a sender or a receiver, one at a time.
For example, communication between a walkie-talkie, wherein at a time only one radio on the channel can transmit. After receiving the message, another radio on the channel replies. This means only one person can talk at a time. It is a two-way radio.
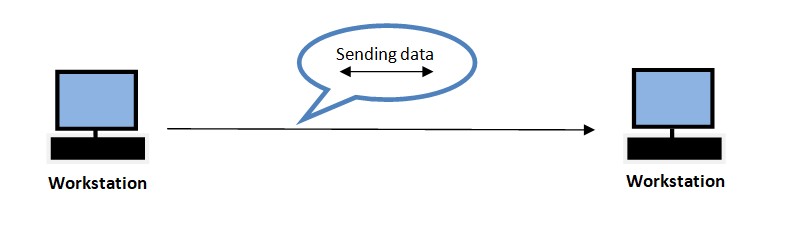
Full Duplex Transmission Mode
Full Duplex mode is a mode in which both sender and receiver can transfer simultaneously.
For example, when you’re having a conversation with anyone on mobile phone, then you can speak and hear at the same time i.e. simultaneously.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now


No Comments