17 Oct Decision Making Statements in C
Decision-making statements in the C language are the same as in other programming languages, such as C++, Java, etc. Decision-making is needed when you want a set of instructions to be executed in one condition and different sets of instructions in another.
Before moving further, we’ve prepared a video tutorial to understand what decision-making statements are in C:
Video: Decision-Making Statements in C
Video: Decision-Making Statements in C (Hindi)
The following are the decision-making statements in C,
- if statement
- if-else statement
- if-else if-else statement
- switch statement
if statement
If the condition is true, the statement gets executed. If the condition is false, it does nothing.
Syntax
The following is the syntax for the if statement in C language,
if(condition true) statement gets executed;
The following syntax is for multiple statements,
if(condition true) {
multiple statement gets executed;
multiple statement gets executed;
}
The following is an example showing the usage of the if statement in C language.
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main() {
int i = 10;
if(i>5)
printf(“The value is more than 5”);
getch();
}
The following is the output, wherein the if statement executes since the value of i is more than 5:
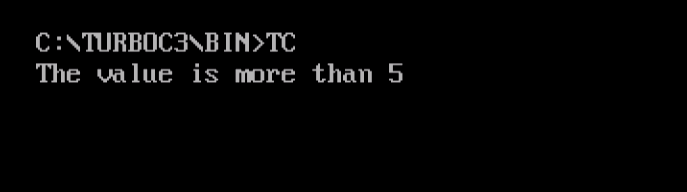
if-else statement
If the condition is true, then a set of statements is executed. If the condition is false, another set of statements gets executed.
Syntax
The following is the syntax for the if-else statements in C language,
if(condition true)
statement gets executed;
else
another statement gets executed;
The following is an example showing the usage of the if-else statement in C language,
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main() {
int i = 2;
if(i>5)
printf(“The value is more than 5”);
else
printf(“The value is less than 5”);
getch();
}
Here’s the output,
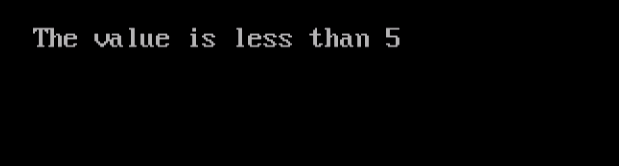
You can also work on nested if-else. Let us see how we can do it for the preceding example,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main() {
int i = 5;
if(i>=5) {
if(i==5) {
printf("The value is equal to 5");
}
else {
printf("The value is more than 5");
}
}
else {
printf("The value is less than 5");
}
getch();
}
The following is the output, showing what value gets displayed while using nested if-else,
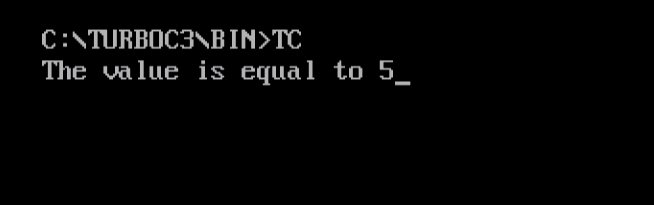
if-else if-else statement
The if-else if-else statement is useful when the if-statement has more than one condition.
Syntax
The following is the syntax for the else-if statements in C languages,
if(condition true)
statement gets executed;
else if()
statement gets executed;
else
another statement gets executed;
The following is an example showing the usage of else-if statement in C languages:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main() {
int i = 20;
if(i>100)
printf(“The value is more than 100”);
else if(i>75)
printf(“The value is more than 75”);
else if(i>50)
printf(“The value is more than 20”);
else
printf(“The value is less than 50”);
getch();
}
The following is the output, displaying the result for values less than 50,
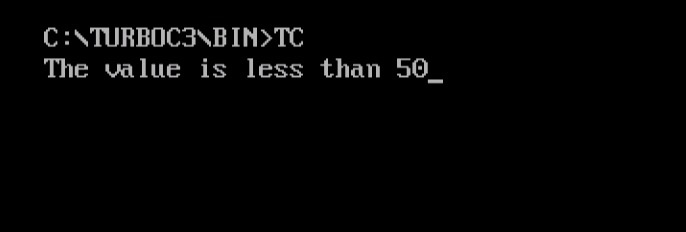
Switch Statement
Use the switch statement if you want to take a decision from more than one choice. For example, grades A, B, C, D, E, etc based on the marks of students.
The following is the syntax:
switch(expression) {
case value1 :
break;
case value2 :
break;
case value3 :
break;
.
.
.
default :
}
The following is an example showing the usage of the switch statement in C language,
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int day = 5;
switch(day) {
case 1:
printf("Monday\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Tuesday\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Wednesday\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Thursday\n");
break;
case 5:
printf("Friday\n");
break;
case 6:
printf("Saturday\n");
break;
case 7:
printf("Sunday\n");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid day\n");
}
return 0;
}
The following is the output:
Friday
In this example, the switch statement checks the value of the day variable and executes the corresponding case block. If none of the case blocks match the value of day, the default block is executed.
This lesson taught us how to work with Decision Making Statements in C Programming. We saw how to implement if, if-else, else-if, and switch statements in C.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others:
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments