14 Jan Data Types in C Programming
In programming, a data type defines the kind of data that can be stored and manipulated within a program. It determines the values that a variable can hold and the operations that can be performed on it.
Before moving further, we’ve prepared a video tutorial to understand what datatypes are in C:
Video: Data Types in C
Video: Data Types in C (Hindi)
C offers a variety of data types that allow you to store different kinds of values. Here’s a breakdown of the primary data types:
- Basic data types
- Derived data types
Basic Data Type
Basic data types are the fundamental data types provided by C. Here’s a breakdown of the basic data types:
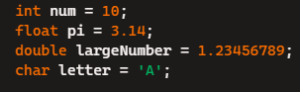
- int: Used for integers. Store integer values.
- float: Used for single-precision floating-point numbers. The size is 4 bytes.
- double: Used for double-precision floating-point numbers. The size is 8 bytes.
Preferred when higher precision is required. - char: Used to store single characters. Strings in C are arrays of chars terminated by a null character.
Here is how we use data types in C:
Derived Data Type
Derived data types are built from the basic data types. Each of these derived data types offers unique ways to store and manipulate data in C:
- Arrays: Collection of elements of the same type.
- Pointers: Variables that store the memory address of another variable.
- Structures (struct): Used to group different data types into a single unit.
- Unions (union): Similar to structures, but they share the same memory location for their members.
- Enumeration (enum): A user-defined data type that consists of integral constants.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others:
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:


No Comments