21 May Morphological Operations (Erosion, Dilation, Opening, Closing) with OpenCV
Morphological operations are image processing techniques that process images based on shapes. They apply a structuring element to an input image, creating an output image of the same size. It is used for noise removal, filling gaps, and separating objects. OpenCV provides several morphological operations that are particularly useful for binary images.
Basic Morphological Operations
- Erosion: Erosion “erodes” the boundaries of foreground objects (white pixels in binary images).
- Dilation: Dilation is the opposite of erosion – it “expands” the foreground objects.
Compound Morphological Operations
- Opening: Opening is erosion followed by dilation. It’s useful for removing noise.
- Closing: Closing is dilation followed by erosion. It’s useful for closing small holes.
Practical Applications
- Noise removal: Opening can remove small noise particles
- Hole filling: Closing can fill small holes in objects
- Edge detection: Morphological gradient can highlight edges
- Feature extraction: Top hat/black hat can extract small elements
Remember that the size and shape of the kernel significantly affect the results, so you’ll need to experiment with different parameters for your specific application.
Let us see an example of implementing Erosion, Dilation, Opening, and losing morphological operations with OpenCV:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
# Morphological Operations (Erosion, Dilation, Opening, Closing) import cv2 import numpy as np # Load a binary/grayscale image image = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\hp\Downloads\Astronaut.png', 0) _, binary = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # Define a kernel (structuring element) kernel = np.ones((5,5), np.uint8) # Erosion (shrinks white regions) eroded = cv2.erode(binary, kernel, iterations=1) # Dilation (expands white regions) dilated = cv2.dilate(binary, kernel, iterations=1) # Opening (erosion followed by dilation - removes noise) opening = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) # Closing (dilation followed by erosion - fills holes) closing = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel) # Display results cv2.imshow("Original", binary) cv2.imshow("Eroded", eroded) cv2.imshow("Dilated", dilated) cv2.imshow("Opening", opening) cv2.imshow("Closing", closing) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
Output
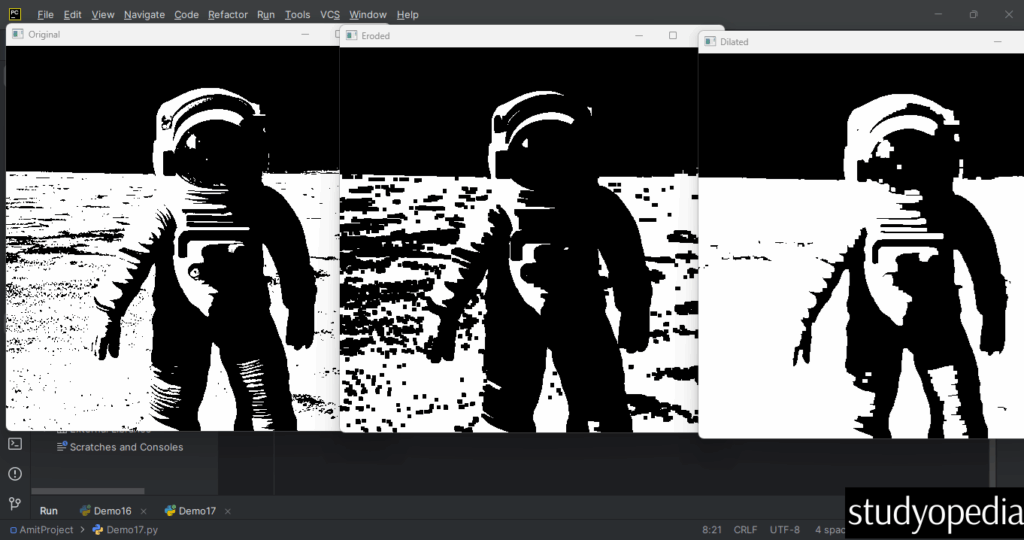
It also displays for other operations:
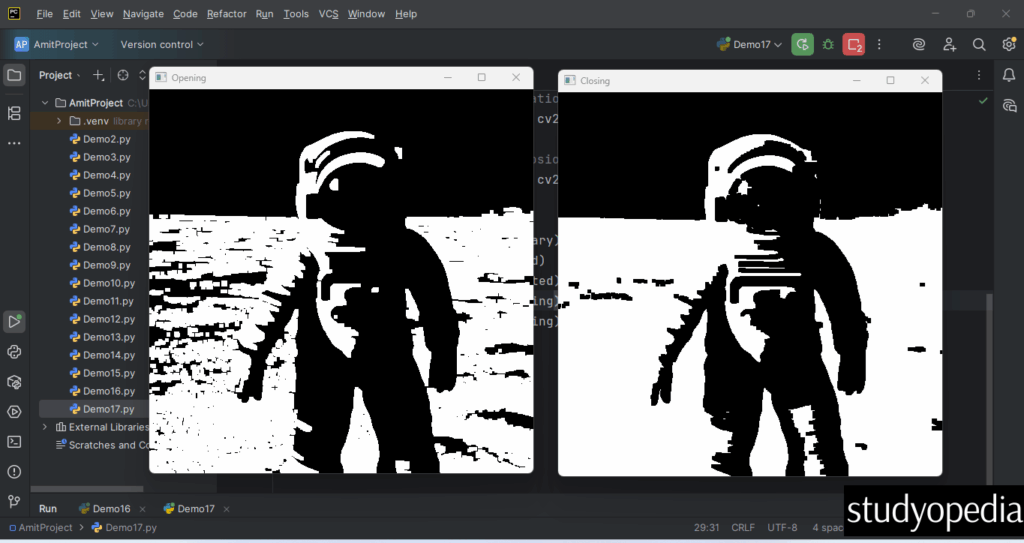
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:
- Apply Sepia Tone filter with OpenCV
- Generative AI Tutorial
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Ollama Tutorial
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Tutorial
- Copilot Tutorial
- Gemini Tutorial
- ChatGPT Tutorial


No Comments