15 Mar Blur an image with OpenCV
Add a soft-focus effect by blurring the image. Use the GaussianBlue() function to blur an image. Let us see an example of blurring an image with OpenCV:
# Read and display an image with OpenCV and make it blur
import cv2
# Load an image
image = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\hp\Downloads\Astronaut.png')
# Apply a Gaussian blur
blurred_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (15, 15), 0)
# Display the result
cv2.imshow("Blur Filter", blurred_image)
# Wait for a key press and close the window
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
The following is the output:
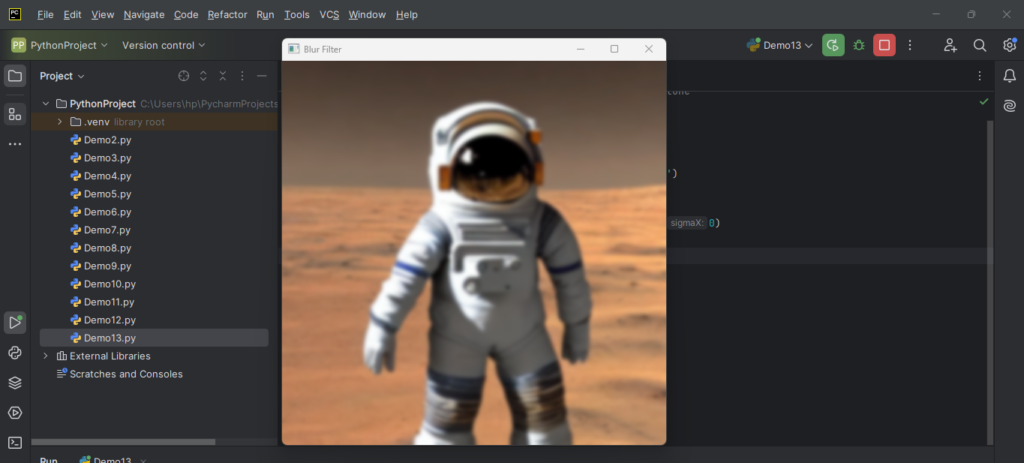
Explanation:
This Python script demonstrates how to use the OpenCV library to load an image, apply a Gaussian blur, and display the result:
- The script starts by importing OpenCV and loading an image from the specified file path using the
cv2.imread()function. - The loaded image is assigned to the variable
image. - A Gaussian blur is then applied to the image using the
cv2.GaussianBlur()function. This function takes three arguments: the image to be blurred, the size of the kernel(15, 15)(which determines the level of blurriness), and the standard deviation in the X and Y directions (set to0to allow automatic calculation). - The blurred image is stored in the variable
blurred_image. - Finally, the script displays the blurred image in a window titled “Blur Filter” using the
cv2.imshow()function. - To allow interaction, the script waits for a key press with
cv2.waitKey(0)before closing the window usingcv2.destroyAllWindows(). - This provides a clear and interactive way to visualize the blurred effect on the image.
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:
- Generative AI Tutorial
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Ollama Tutorial
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Tutorial
- Copilot Tutorial
- Gemini Tutorial
- ChatGPT Tutorial


No Comments