13 Oct What is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is a technique in natural language processing (NLP) coined by Patrick Lewis and his research team in the paper Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks in 2020.
Consider RAG as an approach to enhance the output of LLMs. You would be wondering, how? Well, because RAG provides LLMs with relevant, and fresh data and documents. The data is real-time and context-specific.
RAG includes both retrieval and generation, therefore making it a powerful and awesome tool for applications that need up-to-date, detailed, and context-rich responses. Therefore, let us bifurcate the term RAG:
- Retrieval: Search for relevant data and documents
- Augmented: Adding it to the prompt context
- Generation: Display it as a prompt response
Let us understand a situation where LLM models are used with and without the RAG approach.
LLM Without RAG
Without RAG, the LLM model is the only source of knowledge therefore some issues like hallucinations can occur. The information is old. The below figure will make the things more clear regarding the LLM process:
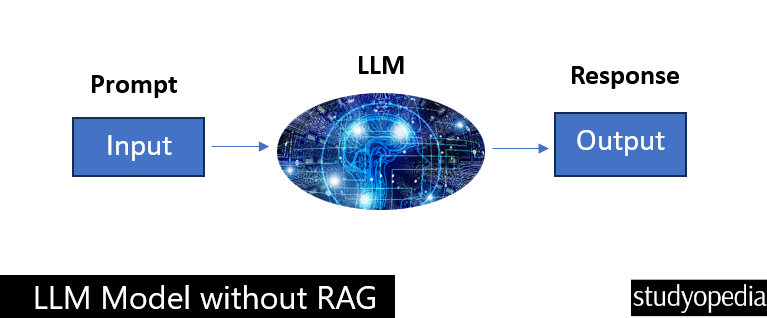
LLM With RAG
With RAG, the LLM model is grounded on source data and the information is always up to date. The data can be public data or specific to your use case.
Grounded on source data means the responses generated by the model are based on, and aligned with, actual information retrieved from reliable sources. The below figure will make the things more clear regarding the LLM with RAG process:
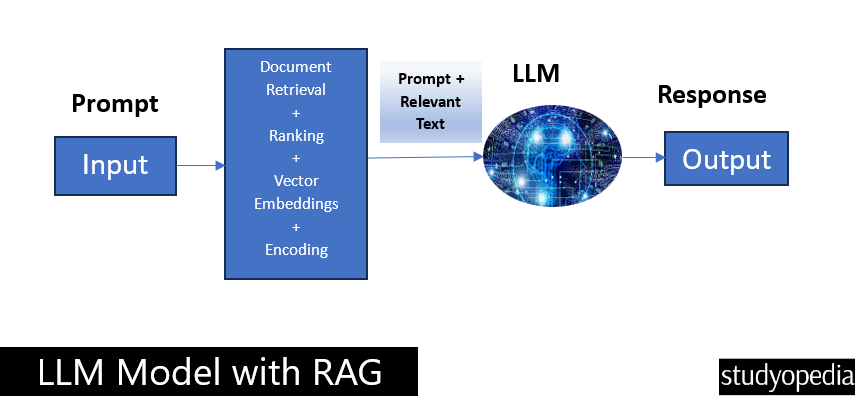
If you liked the tutorial, spread the word and share the link and our website Studyopedia with others.
For Videos, Join Our YouTube Channel: Join Now
Read More:
- What is Deep Learning
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN)
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
- Long short-term memory (LSTM)
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- What is Machine Learning
- What is a Machine Learning Model
- Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised vs Unsupervised vs Reinforcement Machine Learning


No Comments